Batavia slave 'free at last' and honored during Juneteenth service
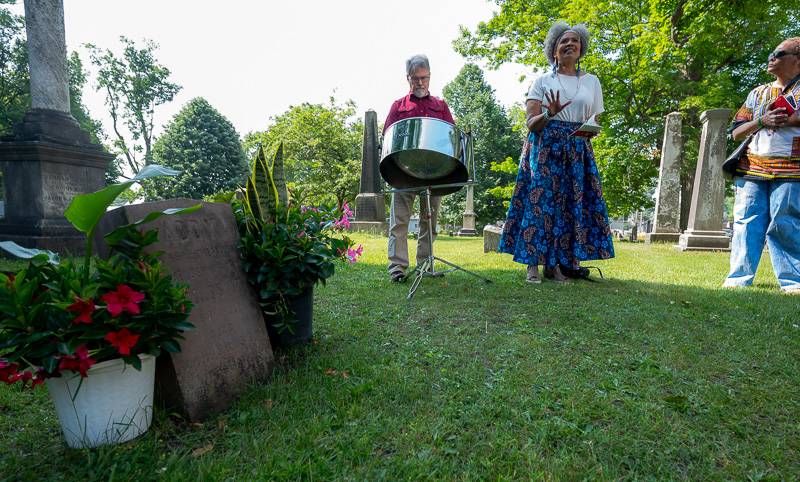
Photo by Howard Owens.
Performing artist Annette Daniels Taylor had planned to review the life that Adeline “Addy” Barbara most likely endured for her 46 years in captivity as a slave in Batavia, but that wasn’t the focus of Monday morning's Juneteenth memorial service, so she turned to a poem titled “Dreaming.”
The piece journeyed back into memories of tall trees, running barefoot, glistening cocoa-brown skin under the hot sun, smiling teeth, beautiful souls, and dancing with one another.
“We danced to drums of waterfalls, drums of hoofbeats, drums of heartbeats, drums of rain storms, drums of drought, drums of baby's breath, drums of aching souls, drums of flying feet, drums of running legs,” Taylor said at the Historic Batavia Cemetery. “Drums without shame, drums without whips, drums without cuffs, drums without ropes, drums without branding irons, I still hear them beating, but only in my dreams, dreams of freedom.”
Addy’s last name was Barbara, though she belonged to the Rev. Lucius Smith, an Episcopal priest who owned her as a member of his family. She was a slave from the tender age of four until she died in 1857 at age 50. The memorial service was to honor and dignify her life for those 46 years in between.
The Rev. Shiela Campbell McCullough performed a memorial service and dramatic reading, proclaiming Addy “free at last.” Way down yonder, in the graveyard walk, I’m gonna meet with my God, and we’re gonna have a talk, she said. “I’m free at last, I’m free at last.”
“Thank God almighty, I’m free at last. And in the words of Harriet Tubman, I’d rather be dead and in the grave than be a slave,” McCullough boldly said in Addy’s spirit. “I’m free at last.”
“Her marker reads Addy for 46 years, the faithful colored servant of the Reverend Lucius Smith and family, died Jan. 28, 1857 … This means that Addy began her burden for the Smith family at the age of four; this is Lucius Smith's marker, very symbolic, as you can see, even in death — even in death — her slave master overlooks her,” McCullough said. “The word servant and this X on her marker, connotes the idea that Addy had a choice. The word servant is an exchange of a kind or pleasant word that is being substituted for an explicit or offensive word. In this context, the use of the word servant camouflages the truth that Addy was indeed a slave. She was the slave of the Episcopal priest, Reverend Lucius Smith. And she was burdened with the lifelong responsibility of sacrificing her own humanity for the benefit of another person.
“The word servant downplays the psychological burden of surrendering one's humanity. So today, as a community, we gather, acknowledging the truth of Addy’s condition. Addy was not a servant, she was a slave,” McCullough said. “We join hands and hearts today to remove the veneer and allow the truth to take its rightful place. Addy was a slave.”
Batavia’s St. James Episcopal and First Presbyterian churches had established plots in the cemetery since 1823, which is why Lucius Smith and his family were buried there. The Rev. Deacon Diana Leiker spoke on behalf of St. James to assure folks that the Episcopal Church is righting those wrongs of the past.
“The church as a whole is working very, very hard with our black brothers and sisters to learn more, to be open to what we did, to help people to heal. We are recognizing all of the despicable, tragic things that were done on behalf of the church or with the church being complicit in letting things happen,” Leiker said. “So we just want you to know that this is wonderful. We had no idea that Lucius Smith owned someone. So we're really thankful that this was being brought to light. And we just want you to know we are doing a lot of hard work nationally.”
Rev. Roula Alkhouri, of Batavia First Presbyterian Church, was one of the organizers of the special Juneteenth event. It came about from McCullough’s pain that bubbled up after learning about Addy. It raised questions of how to move on yet not ignore an important piece of the past.
“What do we do with this pain? What do we do with this history? And so we've been talking and praying and thinking, and so that's kind of like, okay, Juneteenth is coming up, can we celebrate her humanity? Can we look at the story and reclaim it in a different way? And so that's what brought it together for us,” Alkhouri said. “And then we talked, we connected with (Batavia Cemetery Association President) Sharon Burkel, and said, Can we do this? And she said, Absolutely.
“I feel like always, whenever we bring up the hard parts of our lives or our history, it brings healing. You know, it's like, people don't want to talk about the painful stuff. But if you don't, you'd never heal," Alkhouri said. "And if you don't honor the lives of people who suffered, then it gets repeated in different forms. But it does, always, I mean, you see it in families the same way, not just the nation. So we're hoping to be part of that healing for the nation.”
A monetary gift will be used to add another inscription on Addy’s headstone. This will help to tell “a different side of the story and reclaim her humanity and her being created in the image of God,” Alkhouri said.
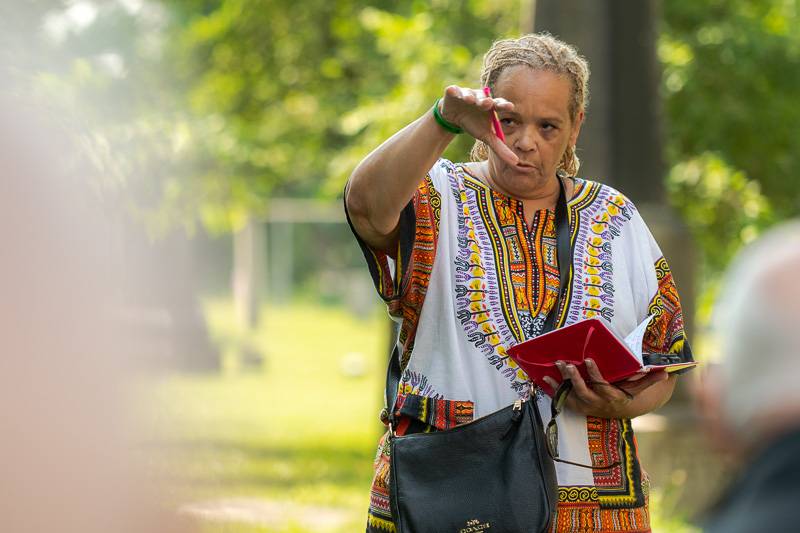

Photo by Howard Owens.
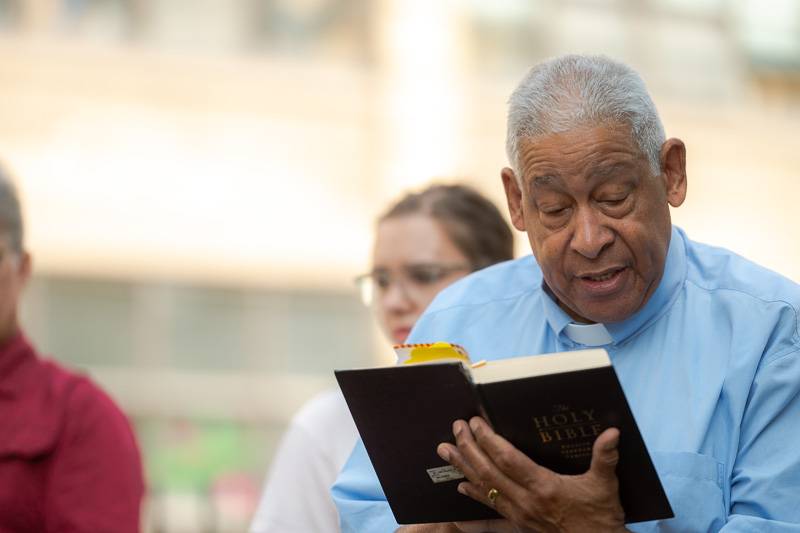

Photo by Howard Owens.
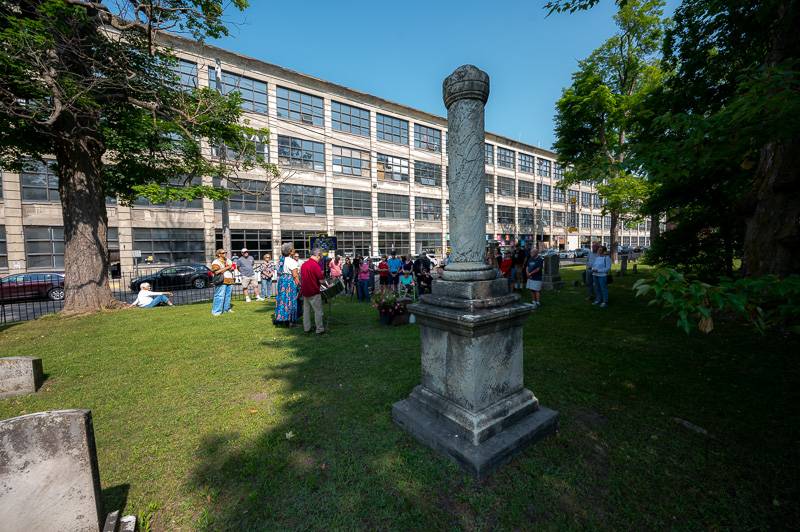

Photo by Howard Owens.
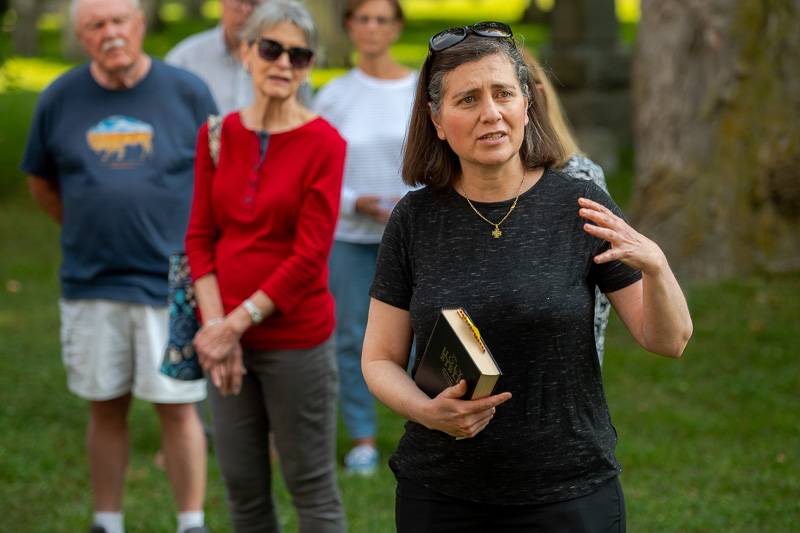
Photo by Howard Owens.
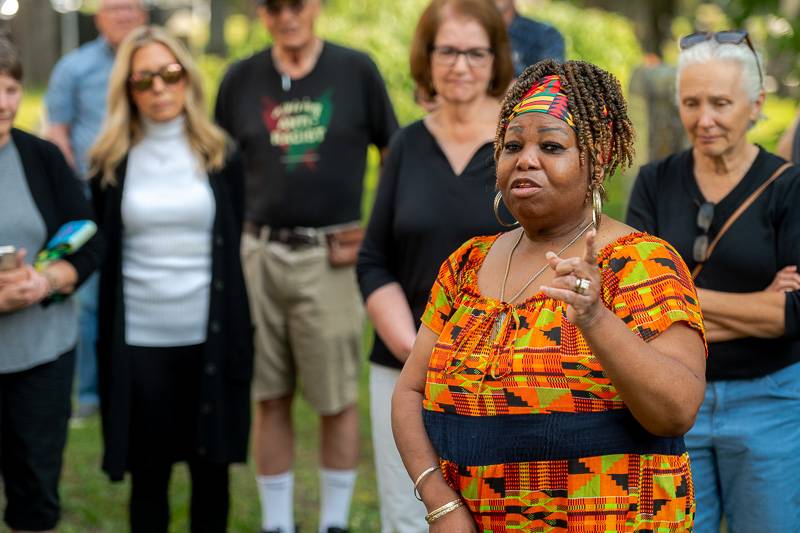
Photo by Howard Owens.
Photo by Howard Owens.

Photo by Howard Owens.
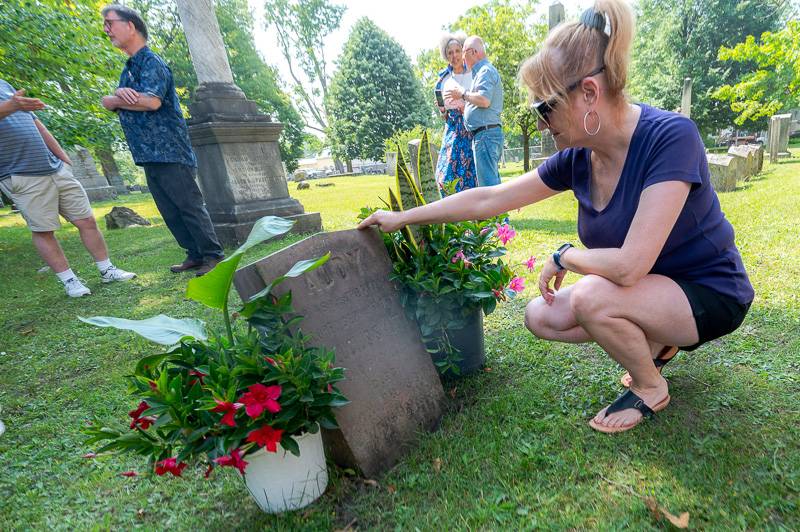

Photo by Howard Owens.
